Keidanren Declaration for Biodiversity and Guideline
Keidanren (Japan Business Federation)
Keidanren Committee on Nature Conservation
Introduced March 17, 2009
Revised October 16, 2018
Revised December 12, 2023
Introduction
In 1992, when the Earth Summit (the United Nations Conference on Environment and Development) was held, Keidanren established the Keidanren Nature Conservation Fund and the Keidanren Committee on Nature Conservation as entities to put the philosophy of the Keidanren Global Environment Charter of 1991 into practice. Since then, Keidanren and the Keidanren Committee on Nature Conservation have engaged in various biodiversity conservation activities.
Until now, Keidanren and the Keidanren Committee on Nature Conservation have sought to promote balance between the environment and the economy by (1) using the Keidanren Nature Conservation Fund to support nature conservation projects in developing nations, particularly in the Asia-Pacific region, and promoting interaction between companies and NGOs, (2) making policy proposals to create an environment conducive to corporate engagement with biodiversity, (3) raising awareness and disseminating information through symposiums and seminars, and (4) publicizing the Japanese business community’s initiatives through interaction with international environmental NGOs and other international organizations.
Meanwhile, at the 15th Meeting of the Conference of the Parties to the Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD COP15) held in December 2022, the Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework (GBF) was adopted as a new set of worldwide targets in place of the Aichi Biodiversity Targets. This formed the basis for Japan to determine its own policy in the form of the National Biodiversity Strategy and Action Plan (2023–2030). Both the GBF and Japan’s national strategy include content focused on companies, requiring the business community to play a greater role in achieving the GBF vision for 2050 of a world living in harmony with nature, as well as establishing a “nature-positive” world that has halted and reversed biodiversity loss by 2030 to set nature on the course toward recovery (i.e., nature conservation and restoration).
Furthermore, the COVID-19 pandemic and extreme weather events in recent years have forced us to reassess the relationship between nature on the one hand and human activities, economies, and societies on the other. Establishing sustainable economies and societies is a major challenge, and meeting this challenge requires companies to take an approach that integrates the goals of green transformation (i.e., the achievement of carbon neutrality), a circular economy, and a nature-positive (i.e., nature conservation and restoration). They must pursue sustainability-oriented management that incorporates a wide range of environmental initiatives (e.g., decarbonization, resource circulation, and conservation and restoration of biodiversity) into their business activities.
In light of the GBF’s adoption as a new set of worldwide targets, along with other major trends both inside and outside Japan as outlined above, Keidanren and the Keidanren Committee on Nature Conservation have revised the Keidanren Declaration for Biodiversity and Guideline in line with the intended objectives when the declaration and guideline were introduced in 2009 and revised in 2018. By promoting and implementing this revised declaration and guideline, Keidanren and the Keidanren Committee on Nature Conservation will work toward building a society in harmony with nature and realizing a sustainable economy and society, while also helping to meet worldwide targets such as the GBF and the UN Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), as well as Japan’s national strategy including its 30by30.
Keidanren Declaration for Biodiversity and Guideline
Targeting a Nature Positive World in 2030
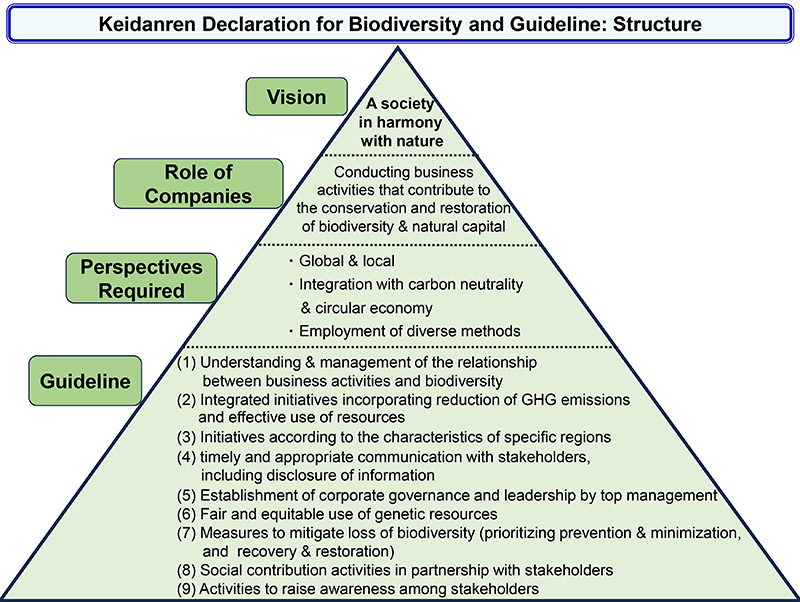
1. Vision
Build a society in harmony with nature.
We will target a society in which people and nature exist in harmony by paying attention to the sustainability of natural capital including biodiversity and ecosystems, and engaging in activities aligned with the natural world.
2. The Role of Companies
To provide goods and services and conduct technological R&D that contribute to the conservation and restoration of natural capital including biodiversity and ecosystems, and to take environmental action throughout supply chains.
As companies, our role in building a society in harmony with nature will be to provide goods and services and conduct R&D that steadily reduce negative impacts on natural capital including biodiversity and ecosystems inside and outside Japan, and instead contribute to increasing positive impacts. In addition, we will take action to conserve and restore natural capital including biodiversity and ecosystems not only within our group companies, but also throughout our supply chains.
3. Perspectives Required
We will maintain both global and local perspectives and take an integrated approach incorporating the goals of carbon neutrality and a circular economy as we work toward a nature-positive (i.e., nature conservation and restoration). In doing so, we will employ a diverse range of methods in line with the characteristics of specific regions and business activities.
We regard the conservation and restoration of natural capital including biodiversity and ecosystems as a challenge that is both global and local. In working toward a nature-positive (i.e., nature conservation and restoration), we will take an integrated approach that incorporates the goals of carbon neutrality and a circular economy and accounts for how these three goals relate to each other. Moreover, we will make use of a diverse range of methods including Nature-based Solutions (NbS).
4. Guideline
To fulfill the role of companies set out above, we will take action to address the following nine areas:
(1) Understanding and management of the relationship between business activities and biodiversity
We will understand and manage the extent to which all our business activities including those throughout global supply chains depend on and influence natural capital including biodiversity and ecosystems, and the associated risks and opportunities.
(2) Integrated initiatives incorporating carbon neutrality and a circular economy
We will tackle challenges such as reducing greenhouse gas emissions, making effective use of resources, and disposing of waste appropriately by implementing integrated initiatives employing a diverse range of methods to conserve and restore natural capital including biodiversity and ecosystems. In doing so, we will take global supply chains and entire product life cycles into account.
(3) Initiatives according to the characteristics of specific regions
Natural capital including biodiversity and ecosystems, and measures to address societal challenges such as regional vitalization and disaster risk reduction, take substantially different forms from one region to another, and the ways in which business activities interact with these also vary. We will employ a diverse range of methods including Nature-based Solutions (NbS) to take environmental action such as utilization of inherent natural capital. As we do so, we will take into account the characteristics of specific regions, including their topographical properties as areas of land, fresh water, or sea, and the extent to which the natural environment has deteriorated, as well as the distinctive features of our own business activities.
(4) Engagement in timely and appropriate communication with stakeholders,
including with disclosure of information
We will make timely and appropriate efforts to provide information and engage in dialogue with consumers, customers, investors, local residents, and a wide range of other stakeholders by actively disclosing information on initiatives aimed at conserving and restoring natural capital including biodiversity and ecosystems.
(5) Establishment of corporate governance and provision of leadership by top management
Alongside working to instill sustainability-oriented management and establish a robust corporate organization and structure, top management and other executives will develop a clear philosophy and vision, and provide leadership.
(6) Fair and equitable use of genetic resources
We will adhere to domestic measures (ABS guidelines) based on the Nagoya Protocol on Access and Benefit Sharing in utilizing genetic resources and sharing associated profits, and comply with laws enacted by the relevant provider country when acquiring genetic resources.
(7) Measures to mitigate loss of biodiversity
nitiatives to conserve and restore natural capital including biodiversity and ecosystems will wherever possible be implemented in the worksites where business activities take place. Maintaining dialogue with local stakeholders, we will prevent and minimize loss of biodiversity, and recover and restore natural functions, primarily in our worksites. If there is no option but to resort to methods involving trading or compensation (offsetting) based upon assessment of biodiversity, we will thoroughly evaluate the effectiveness of such methods.
(8) Social contribution activities
Even if it is difficult to identify a relationship between our own corporate activities and the conservation and restoration of natural capital including biodiversity and ecosystems, we will still engage in social contribution activities. We will engage in such activities through partnerships and collaborations—including provision of funding—with NGOs, local communities and residents, employees, and a diverse range of other stakeholders.
(9) Activities to raise awareness
We will partner with organizations including schools, research institutes, NGOs, and national and local government entities to conduct activities aimed at raising awareness among consumers, local residents, and employees in order to promote recognition throughout society of the need for conservation and restoration of natural capital including biodiversity and ecosystems.